Inspirating Tips About Trial Balances Accounting
A trial balance ensures mathematical accuracy in a company’s financial records by presenting a snapshot of debits and credits for a specific period.
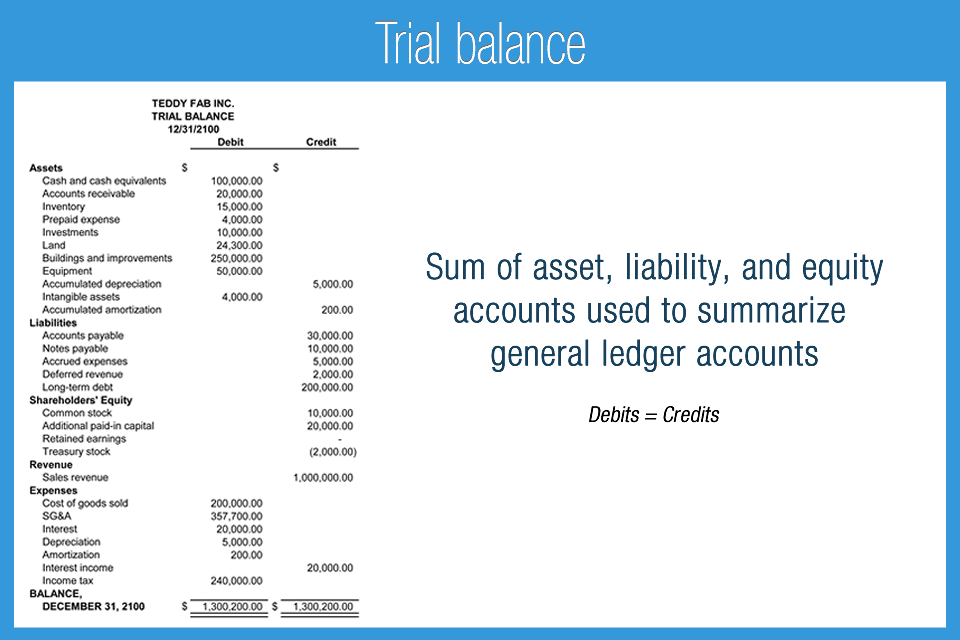
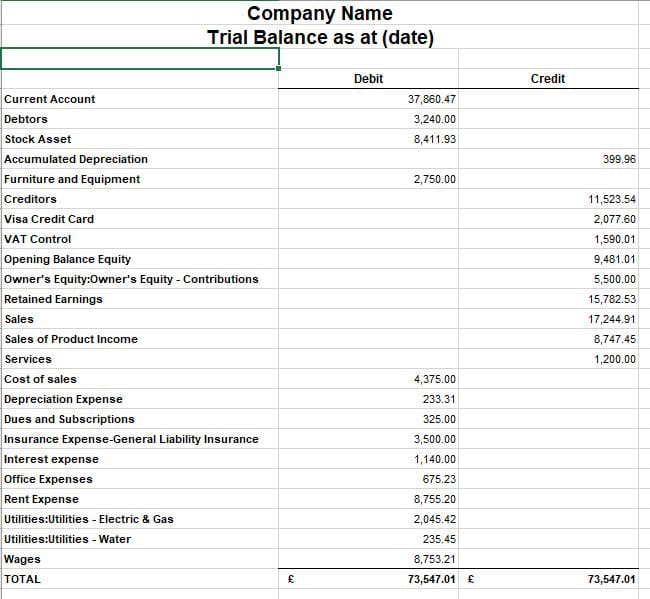
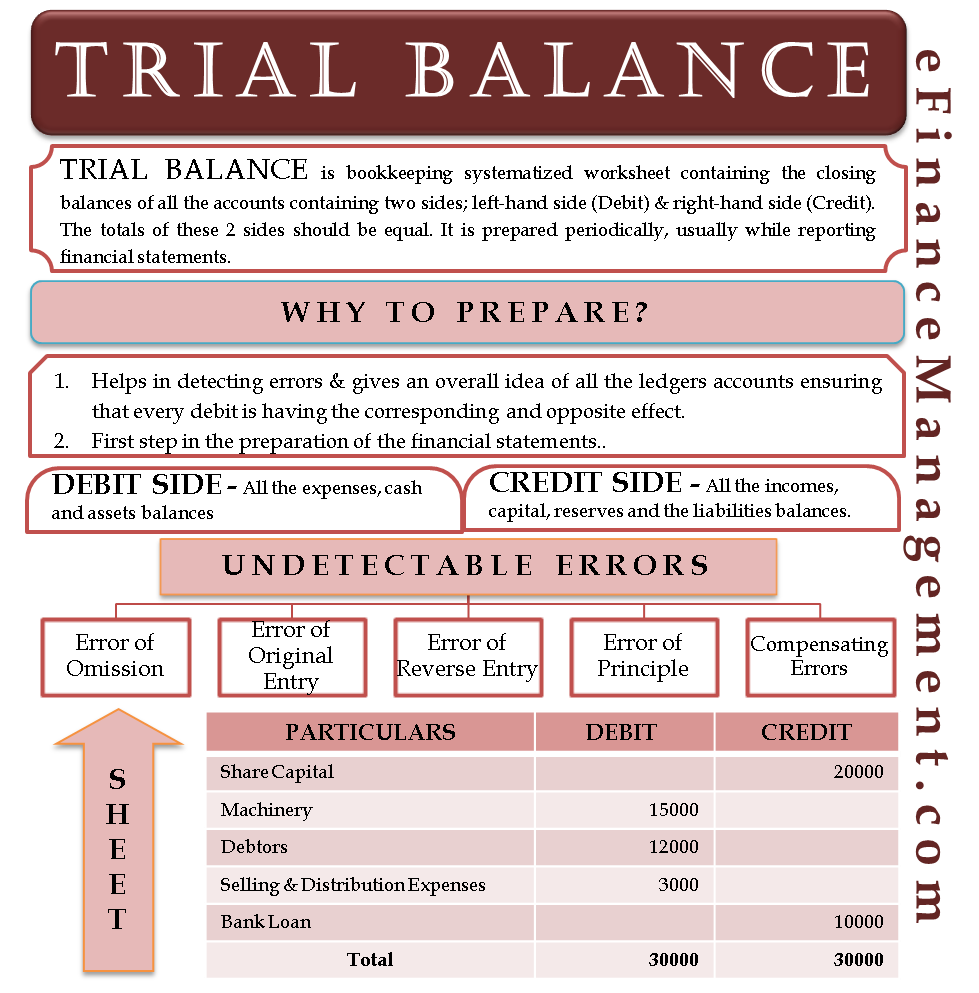
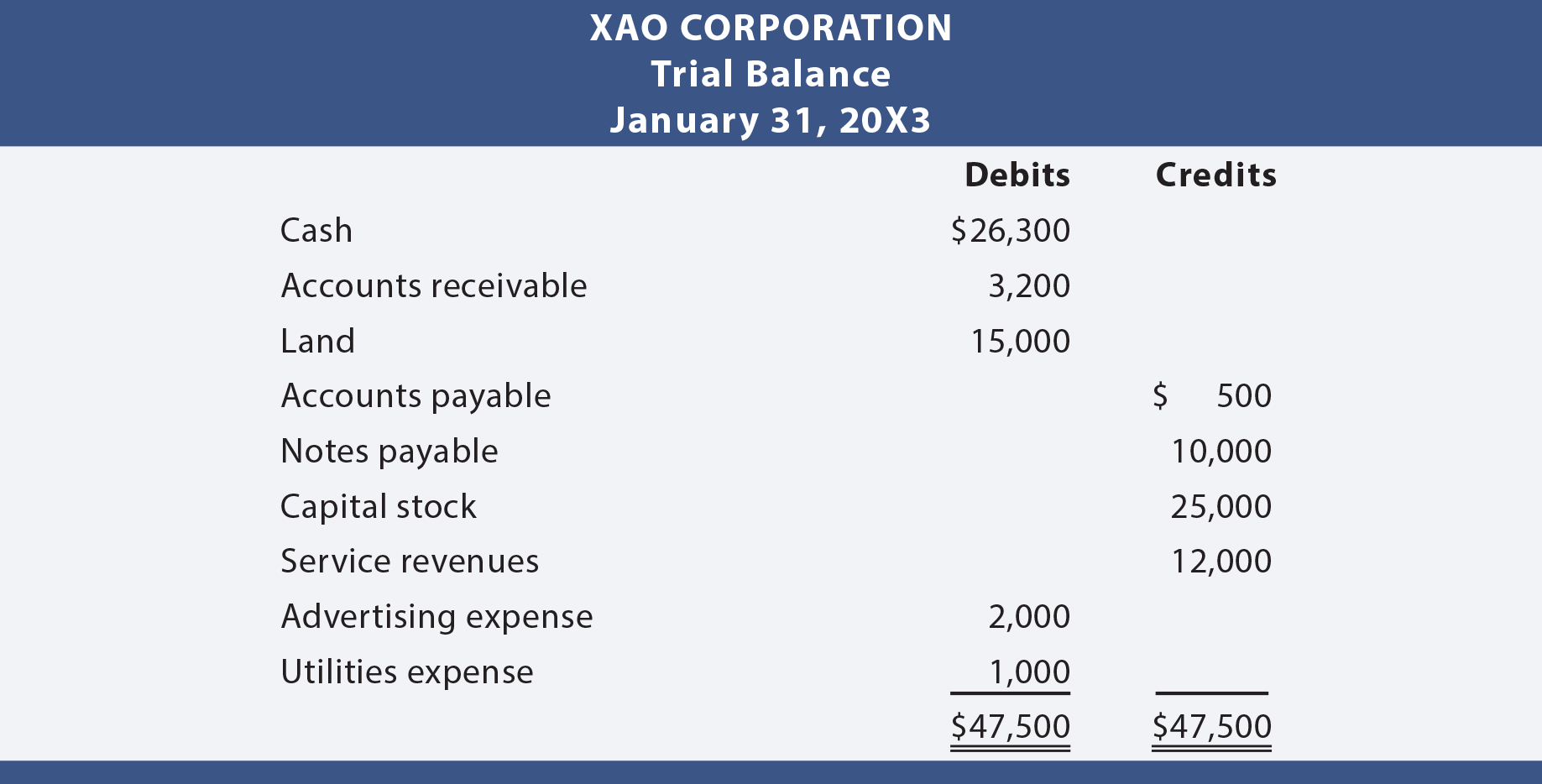
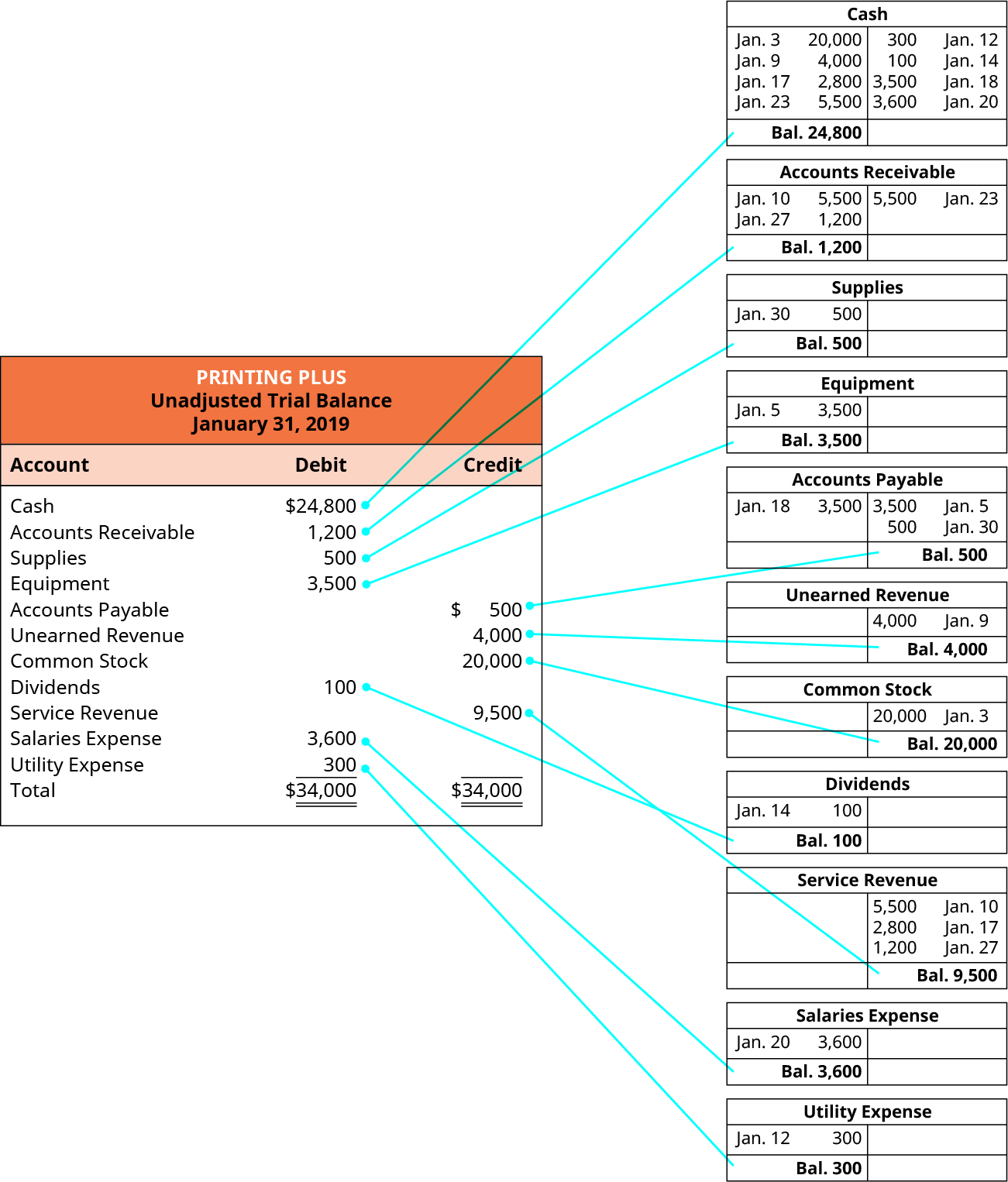
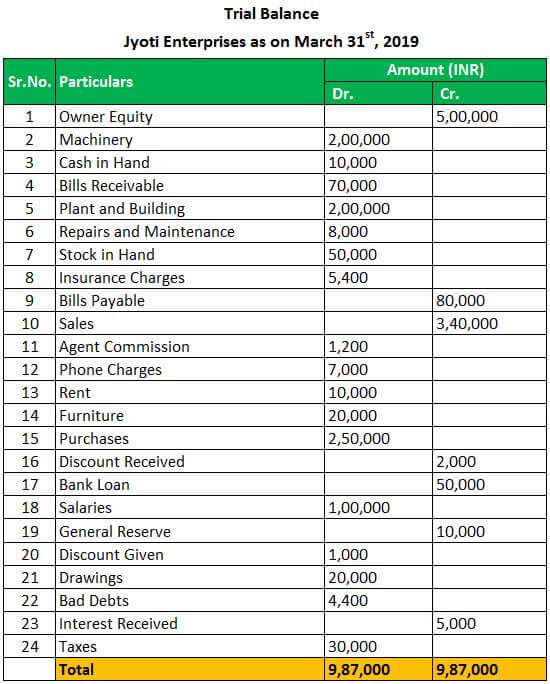
Trial balances accounting. The balances are usually listed to achieve equal. The goal is to confirm that the sum of all debits equals the sum of all credits and identify whether any entries have been recorded in the wrong account. The trial balance is an accounting report that lists the ending balance in each general ledger account.
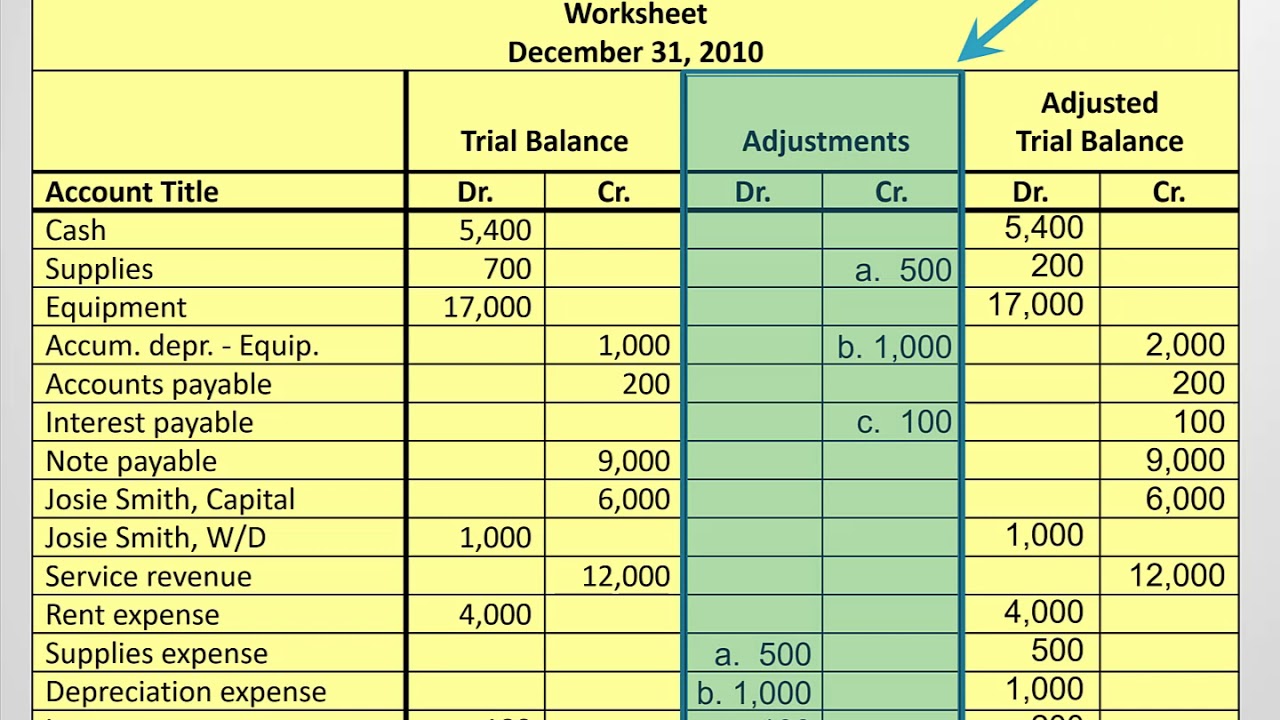
What’s the role of a trial balance in accounting? The trial balance is useful for checking the arithmetic accuracy and correctness of the bookkeeping entries. (often the accounts with zero balances will not be listed.)
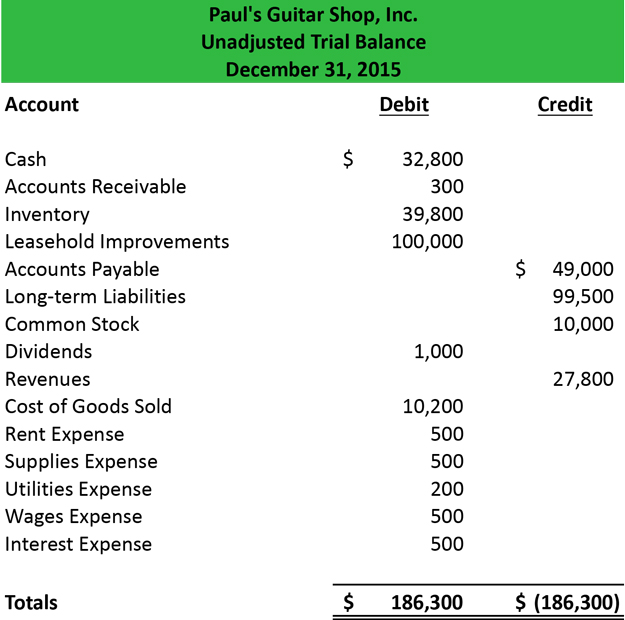
A trial balance is a report that lists the balances of all general ledger accounts of a company at a certain point in time. Preparing an unadjusted trial balance is the fourth step in the accounting cycle. A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet in which the balances of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit account column totals that are equal.
This list will contain the name of each nominal ledger account in the order of liquidity and the value of that nominal ledger balance. A trial balance is an internal financial statement that lists the adjusted closing balances of all the general ledger accounts (both revenue and capital) contained in the ledger of a business as at a specific date. A trial balance simply shows a list of the ledger accounts and their balances.
It is a statement of debit and credit balances that are extracted on a specific date. The total of both should be equal. A trial balance, sometimes abbreviated to tb, is a list of all the account balances in the accounting records on a particular date.
Trial balance refers to a part of a financial statement that records the final balances of the ledger accounts of a company. A trial balance sheet is a report that lists the ending balances of each account in the chart of accounts in balance sheet order. A trial balance is a financial accounting document that lists the balances of all the general ledger accounts of a company at a specific point in time.
Trial balances are a vital auditing technique used to ensure whether the total debit equals the total credit in the general ledger accounts, which plays a crucial role in creating the balance sheet and other financial statements. A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet in which the balances of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit account column totals that should equal each other. The trial balance trial balance trial balance is the report of accounting in which ending balances of a different general ledger are presented into the debit/credit column as per their balances where debit amounts are listed on the debit column, and credit amounts are listed on the credit column.
An organisation prepares a trial balance at the end of the accounting year to ensure all entries in the bookkeeping system are accurate. A trial balance in accounting is a foundational tool that validates the accuracy of financial records. Embark on a journey to understand trial balance, a fundamental concept in accounting.
A company prepares a trial balance. It’s used at the end of an accounting period to ensure that the entries in a company’s accounting system are mathematically correct. Trial balance is a list of closing balances of ledger accounts on a certain date and is the first step towards the preparation of financial statements.
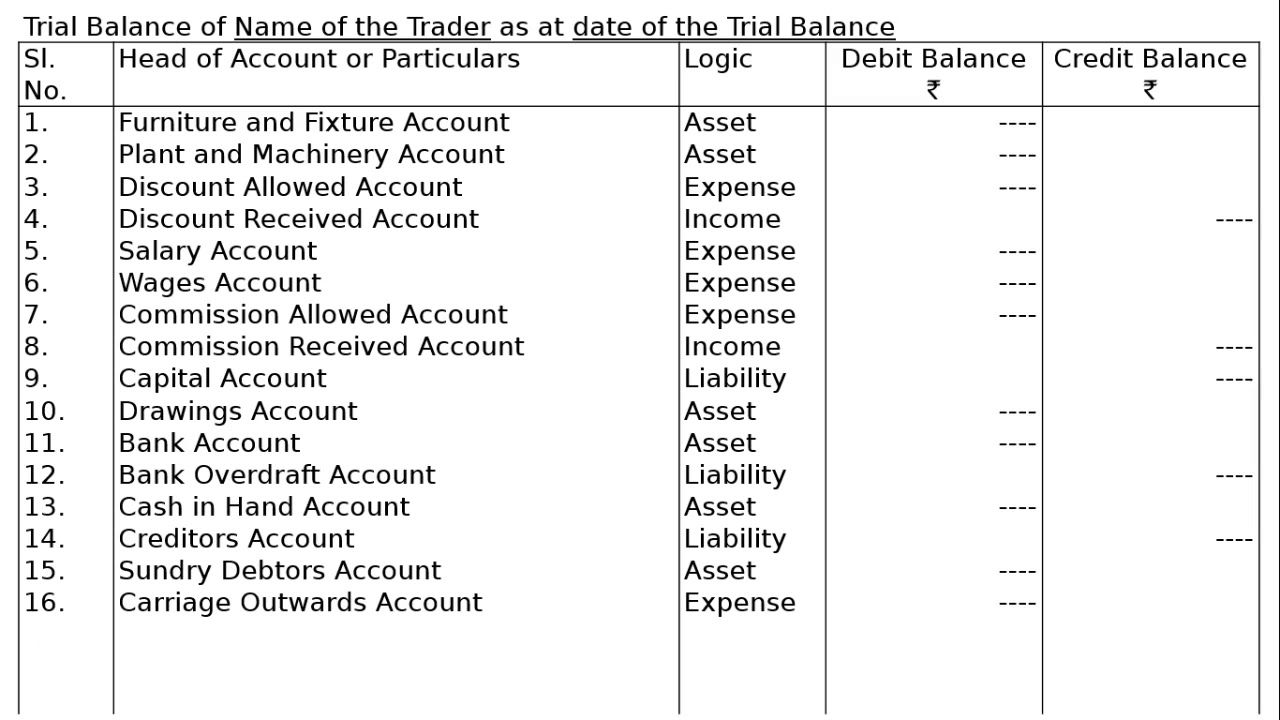
Its purpose is to test the equality between total debits and total. The accounts reflected on a trial balance are related to all major accounting items, including assets , liabilities, equity, revenues, expenses ,. What is a trial balance?




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/trial-balance-4187629-1-c243cdac3d7a42979562d59ddd39c77b.jpg)