One Of The Best Info About Small Business Financial Statements Difference Between Current Tax And Deferred With Example

A tax provision is comprised.
Small business financial statements difference between current tax and deferred tax with example. For example, if your company paid its taxes in full and then received a tax deduction for that period, that unused deduction can be used in future tax filings as a. Deferred tax is the tax effect of timing differences. Tax on profit is immediate, current tax is ongoing, and deferred tax deals.
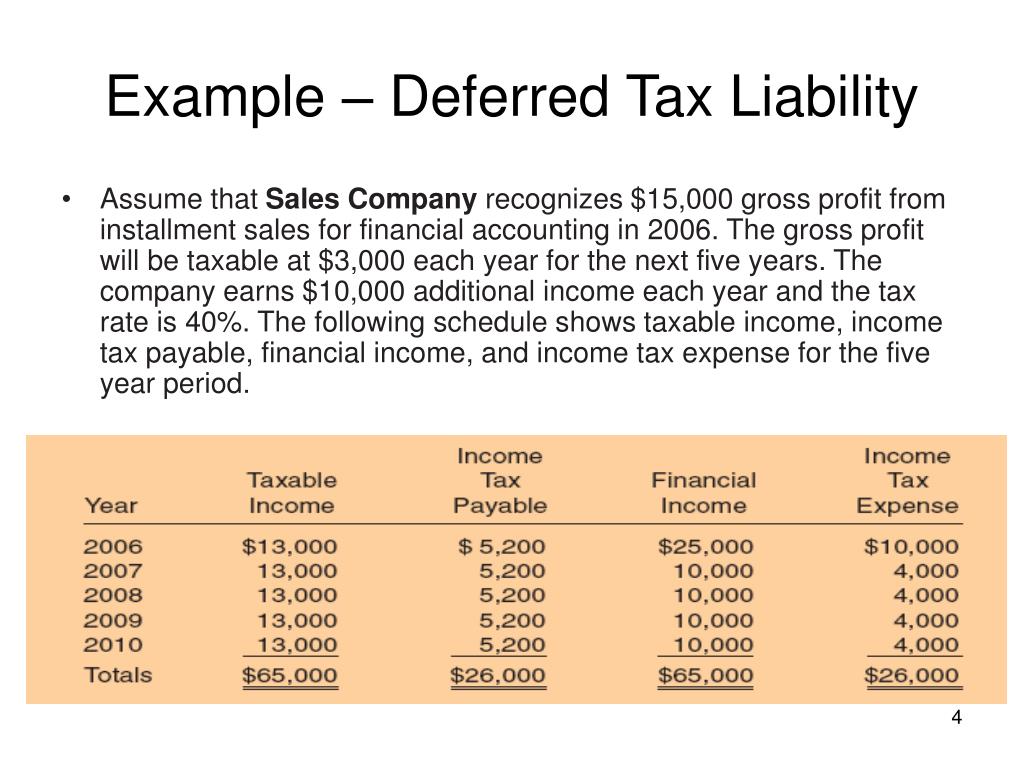
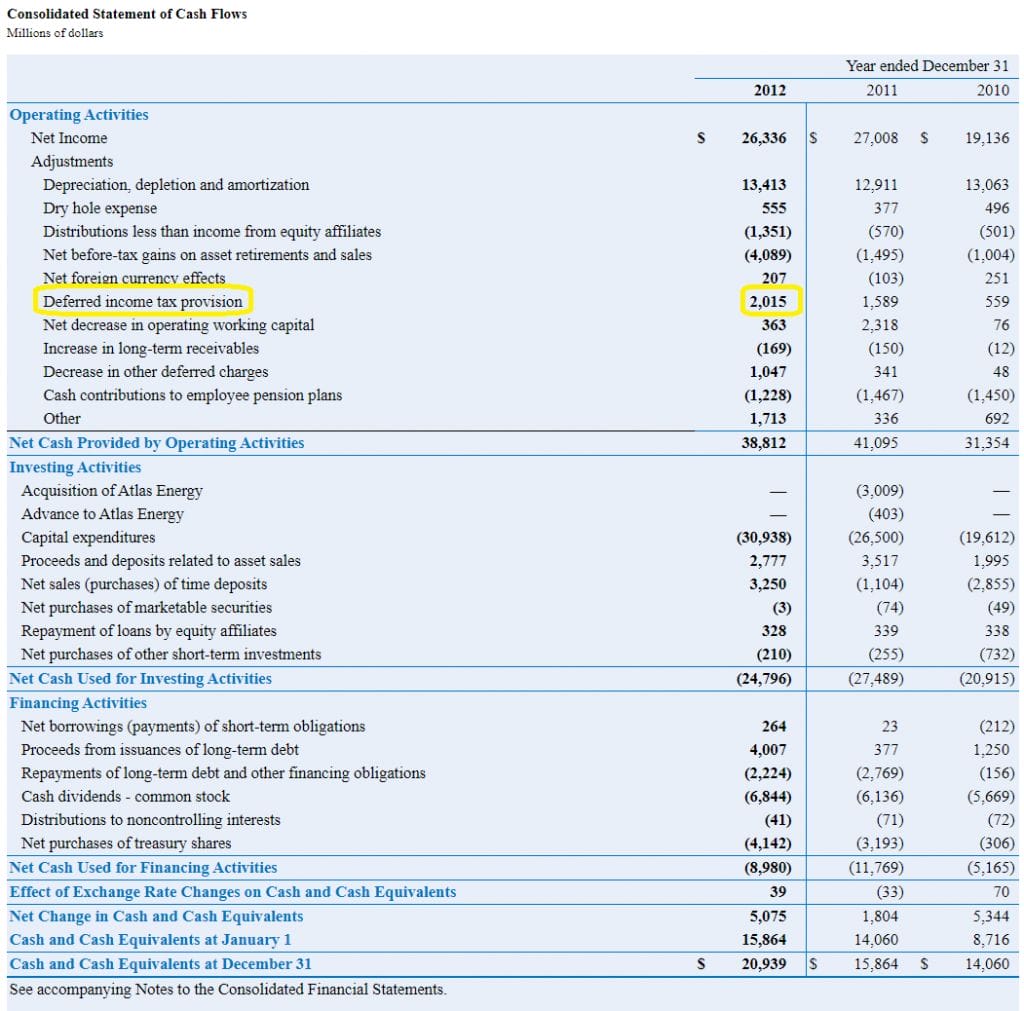
In this lesson, we will explain how to calculate the income tax expense, current taxes payable/receivable, and deferred tax liabilities/assets to be reported in financial. This article will highlight some of the important aspects of an income tax provision and how it clarifies gaap financial statements. A deferred income tax is a liability recorded on a balance sheet resulting from a difference in income recognition between tax laws and the company’s accounting.
It can be either of the following: Deferred tax asset is the amount of tax a business shall pay less in future due to the fact that (a) revenues that are taxed today shall not be taxed in future (when. Dingle limited made a provision of €230,000 for corporation tax on profits for the.
Deferred tax assets are intangible assets that represent potential future tax benefits for a company. The following chart illustrates when an accounting asset or liability (excluding income tax accounts) generates a corresponding deferred tax asset or liability:. Tax on profit, current tax, and deferred tax each play distinct roles in a company’s finances.
Deferred tax liabilities are recognised for all taxable temporary differences (subject to initial recognition exemption) that arise when: Introduction frs 102, the financial reporting standard applicable in the uk and republic of ireland deals with deferred tax in section 29 income tax. As you can see, from a tax perspective the tax payable would be $30 higher than the tax.
They exist on the balance sheet. Income tax expense represents the sum of the tax currently payable and deferred tax. Under/over provision of tax let’s look at an example of how this works:
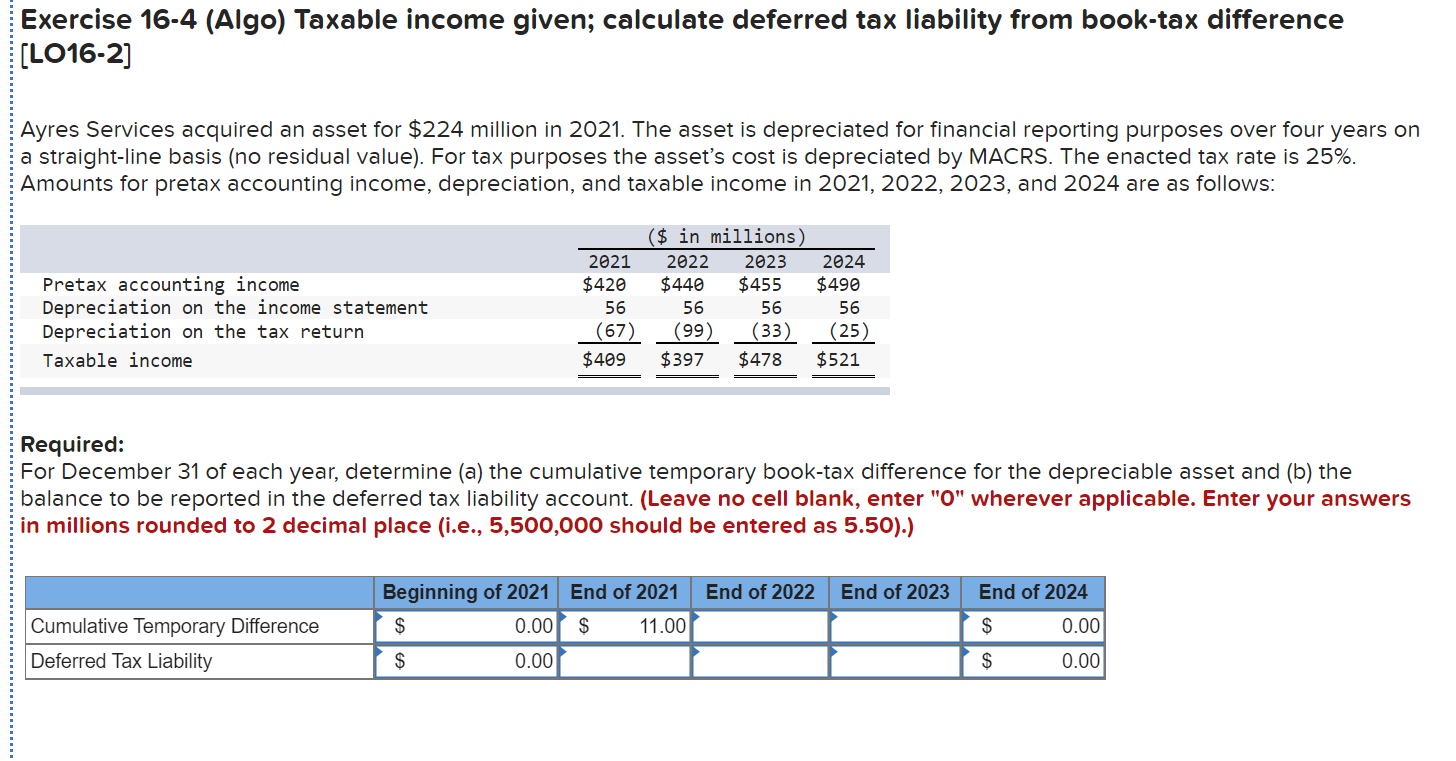
A deferred tax liability (dtl) or deferred tax asset (dta) is created when there are temporary differences between book (ifrs, gaap) tax and actual income tax. The carrying amount of an asset exceeds its tax base, or 2. Company abc realised a profit before tax of r100,000 and paid r20,000 in provisional taxes for the year ended 31 march 20×2.
The carrying amount of a liability is less than its tax base. Temporary differences are the differences between taxable income and.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_DeferredTax_V2-d5ae6ed922204f7eaa8bfb6b7b4b7f44.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2022-04-26at10.45.59AM-aab9d8741c8f4ee1aff95f057ca2ab3a.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/financialstatements-final-d1268249b5284b3989c979ee82f2869e.png)