Beautiful Work Info About Contingent Liabilities On Balance Sheet
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/contingentliability-Final-84e09f386f114ab0b786c4a2ad5bad18.jpg)
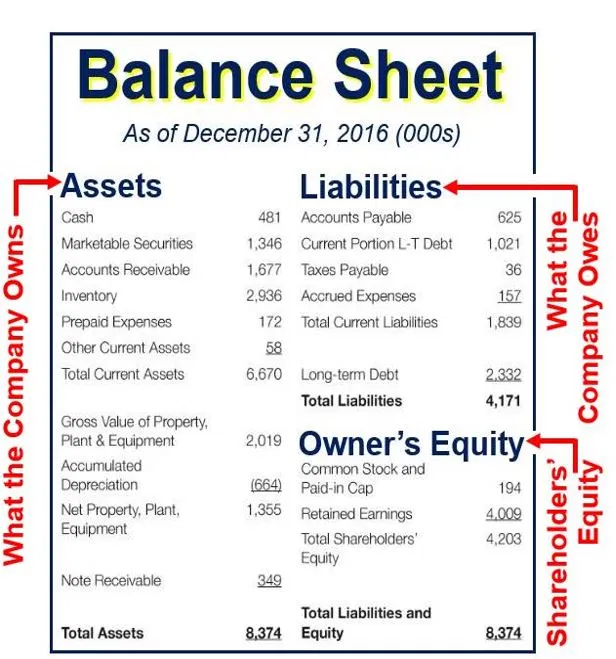
Remember the balance sheet formula:
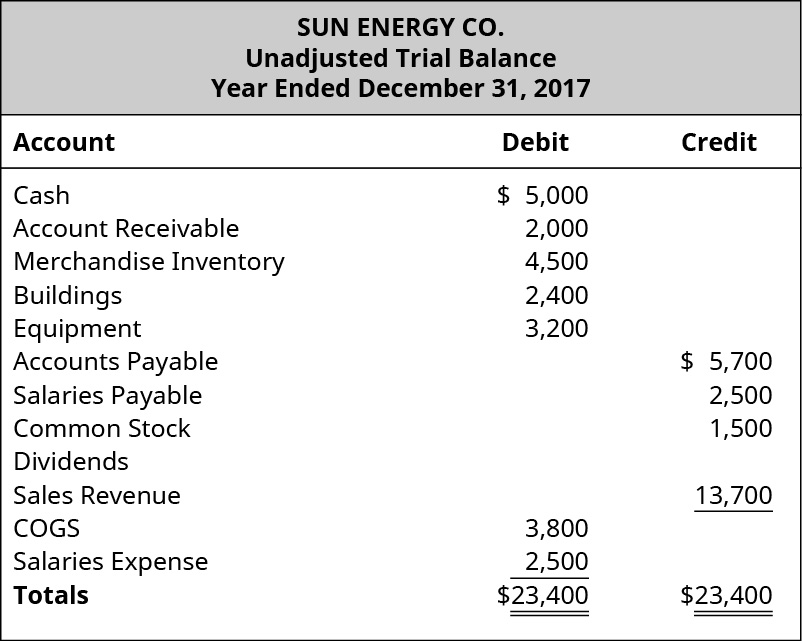
Contingent liabilities on balance sheet. The liability may be a legal obligation or a constructive obligation. Contingent liabilities are liabilities that depend on the outcome of an uncertain event. In simple words, contingent liability is defined as future obligations or liabilities that may or may not arise due to uncertain events or situations.
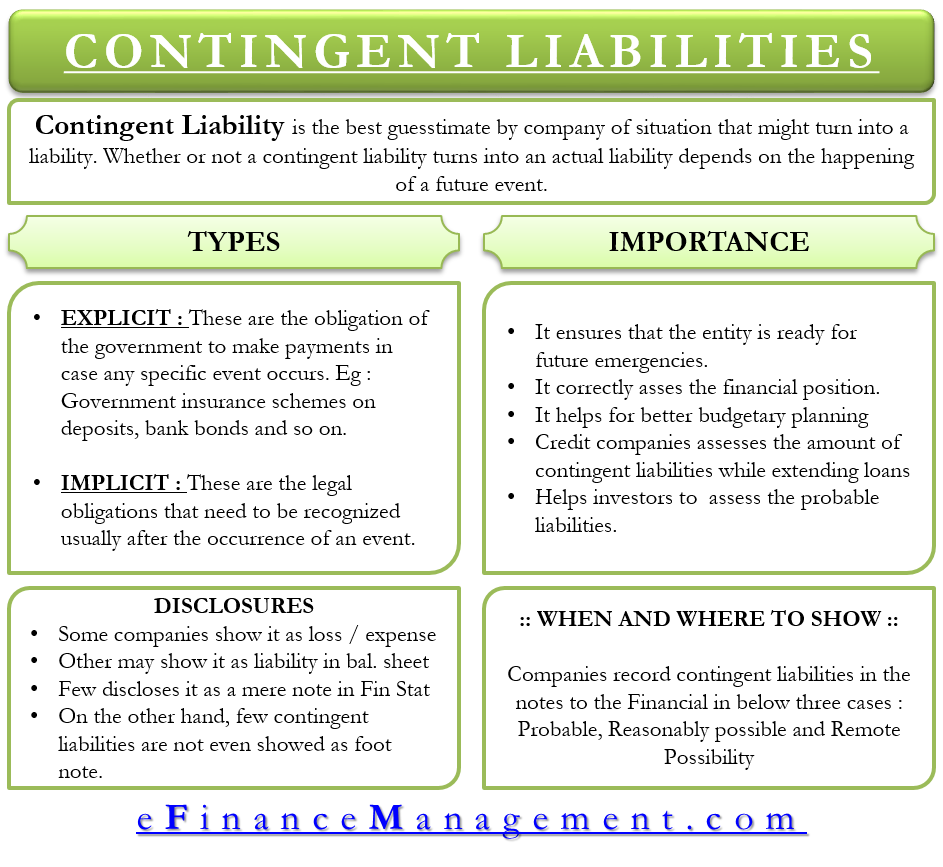
A contingent liability is a potential loss that may occur at some point in the future, once various uncertainties have been resolved. A potential or contingent liability that is both probable and the amount can be estimated is recorded as 1) an expense or loss on the income statement, and 2) a liability on the balance sheet. On a company’s balance sheet, owners’ equity shows what the owners of the business (or shareholders) would have if the company paid off all its debt with its assets.
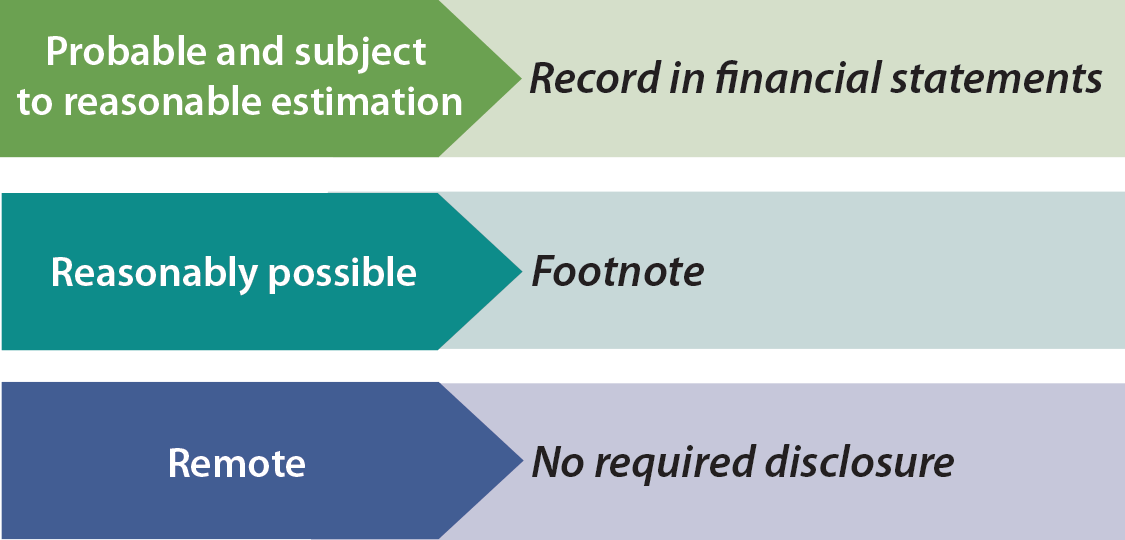
Contingent liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet only if the conditional event is likely to occur and the liability can be reasonably estimated. Ias 37 outlines the accounting for provisions (liabilities of uncertain timing or amount), together with contingent assets (possible assets) and contingent liabilities (possible obligations and present obligations that are not probable or not reliably measurable). The payment and the amount of this liability is uncertain until the event occurs or fails to occur.
Exposure draft e10 contingencies and events occurring after the balance sheet date: Like many other companies, contingent liabilities are carried on google’s balance sheet, report expenses related to these contingencies on its income statement, and note disclosures are provided to explain its contingent liability treatments. This standard shall be applied by all entities in accounting for provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets, except:
A contingent liability is a liability that may occur depending on the outcome of an uncertain future event. Ias® 37, provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets appears to be less popular than other standards because, usually, answers to financial reporting (fr) questions require a balanced discussion of whether criteria are met, as opposed to calculating numbers. Those bonds are thus listed as liabilities on the company’s balance sheet.
Opposite from contingent assets, contingent liabilities are recorded into balance sheet if they are highly likely and the amount can be estimated. A contingent liability is a potential liability that may or may not occur, depending on the result of an uncertain future event. What is net worth or owners’ equity?
A contingent liability can produce a future debt or negative obligation for the company. Ias 37 defines and specifies the accounting for and disclosure of provisions, contingent liabilities, and contingent assets. The exact status of a contingent liability is important when determining which liabilities to present in the balance sheet or in the attached disclosures.
This liability is not yet an actual, confirmed obligation. Here are the ways to record various contingent liabilities. What is a contingent liability?
It prevents the company from ignoring the possibility of contingent liabilities. Some examples of contingent liabilities include pending litigation (legal action), warranties, customer insurance claims, and bankruptcy. Liability is an obligation between one party and another not yet completed or paid for in full.
Ias 10 (1978) was reformatted: These obligations are likely to become liabilities in the future. The relevance of a contingent liability depends on the probability of the contingency becoming an actual liability, its timing, and the accuracy with which the amount associated with it can be estimated.