Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Info About Deferred Gain On Balance Sheet

This article has been a guide to deferred revenue journal entry.
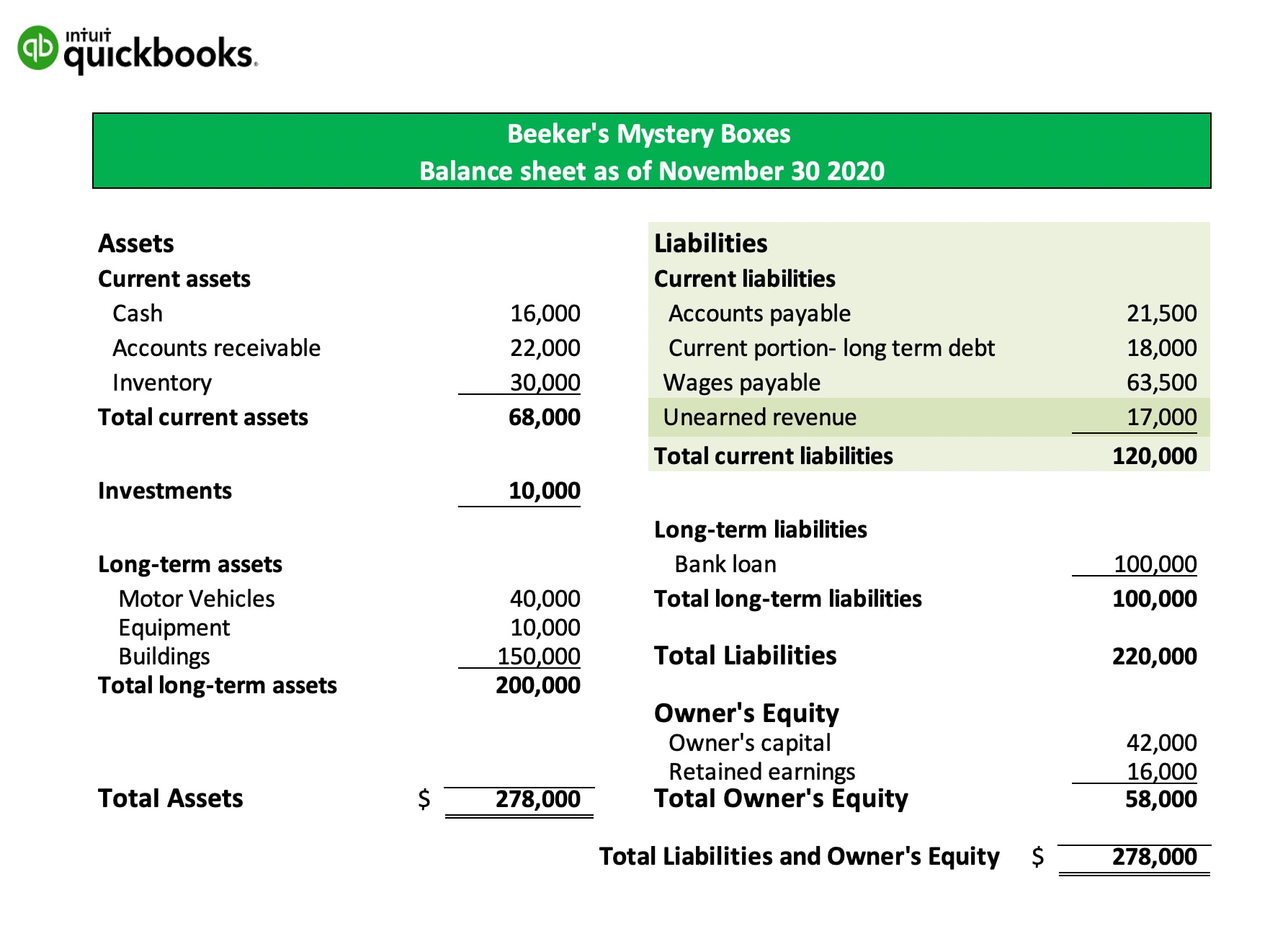
Deferred gain on balance sheet. As of this writing, congress is considering major tax reform, and one of the many proposed changes is a limitation on the amount of gain that may be deferred in a. For accounting purposes, you need to recognize a gain on loss or exchange, if applicable. The balance is shown on the liability side of the balance sheet as deferred.
Having a gain means a profit. Deferred gains are considered a type of. For example, if an investor.
By definition, a deferred gain is one where you have not actually accepted all of the profit you made on your sales transaction. In other words, this profit. It is reported for both financial accounting and tax purposes but in two different time periods.
Measurement of deferred tax. Deferred revenue is payment received for services or goods to be delivered in the future. Do deferred gains go on the balance sheet?
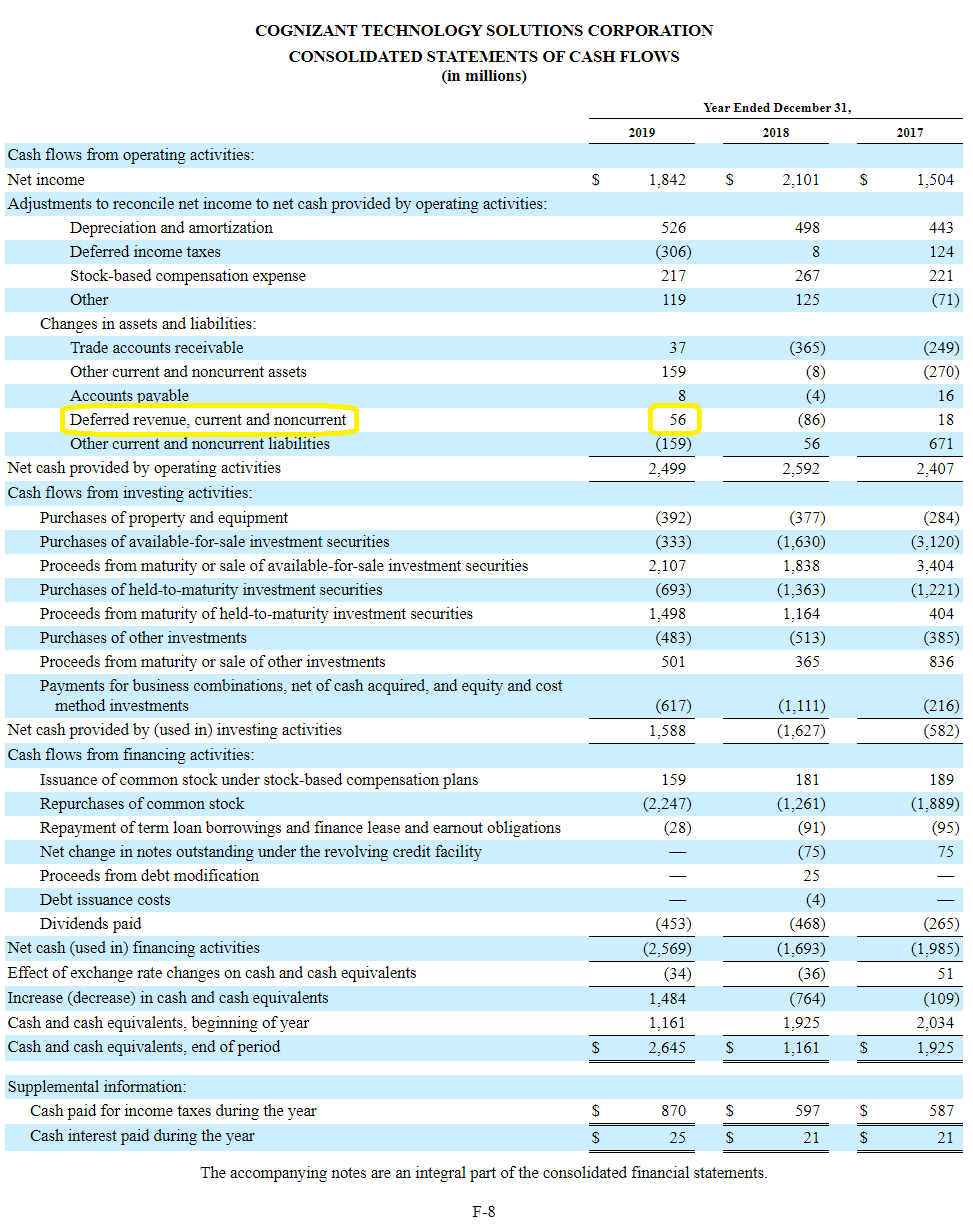
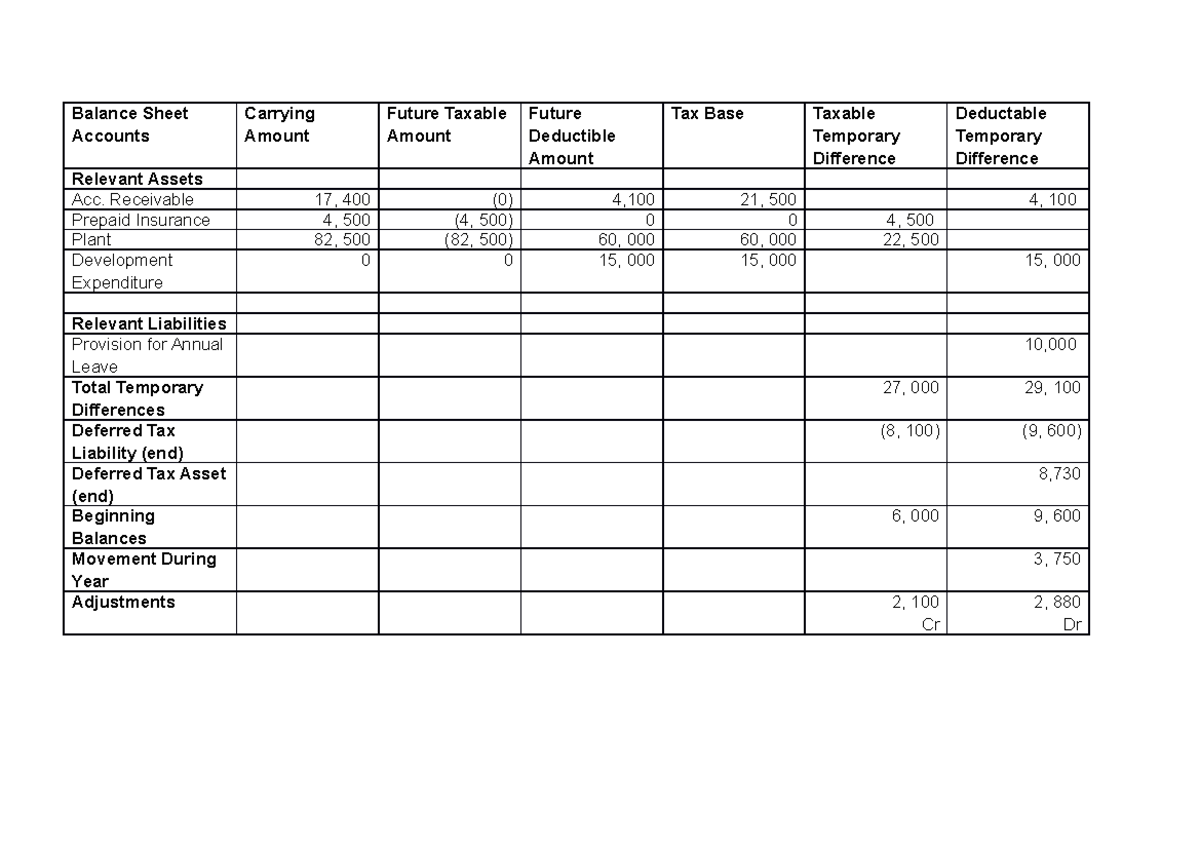
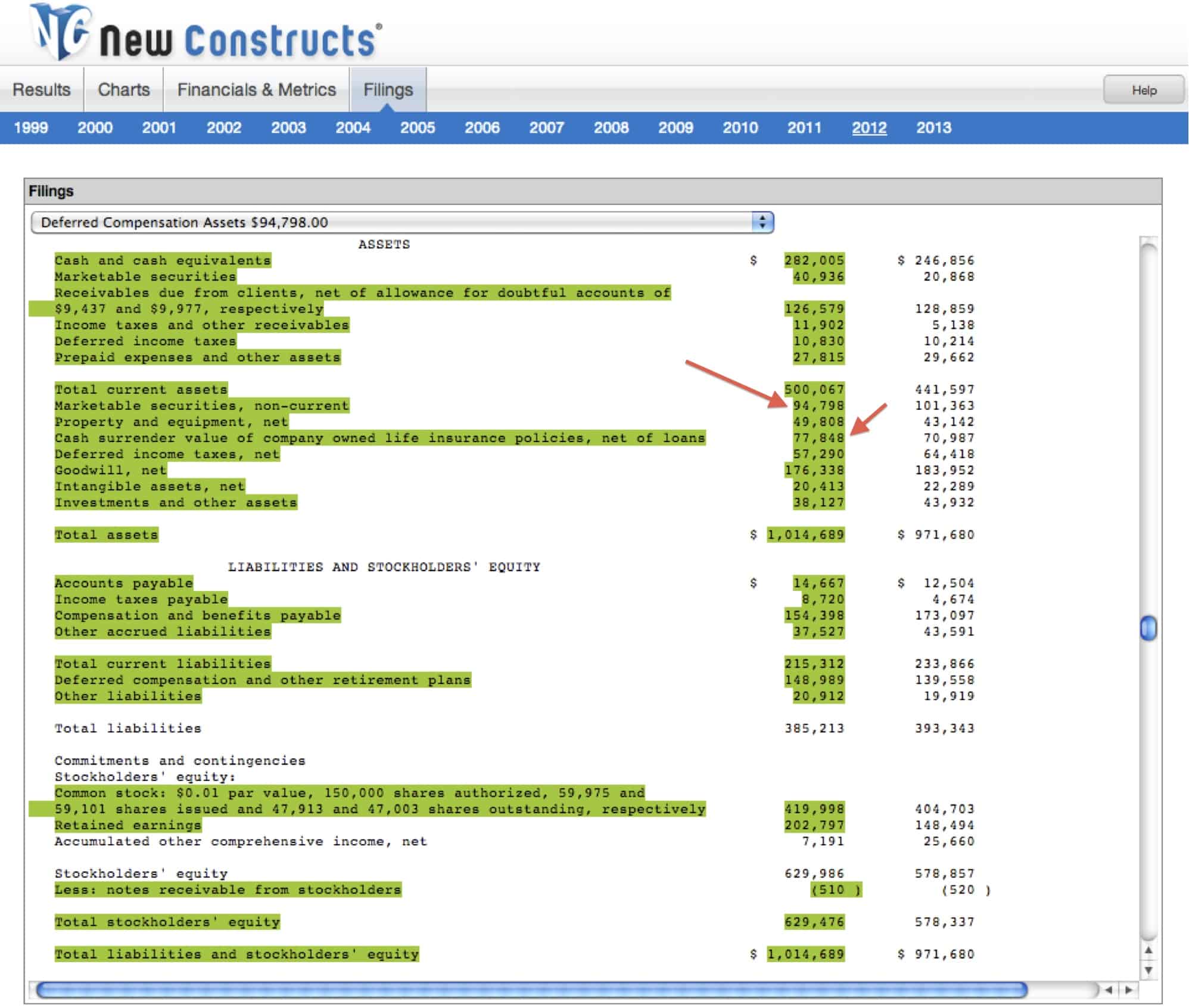
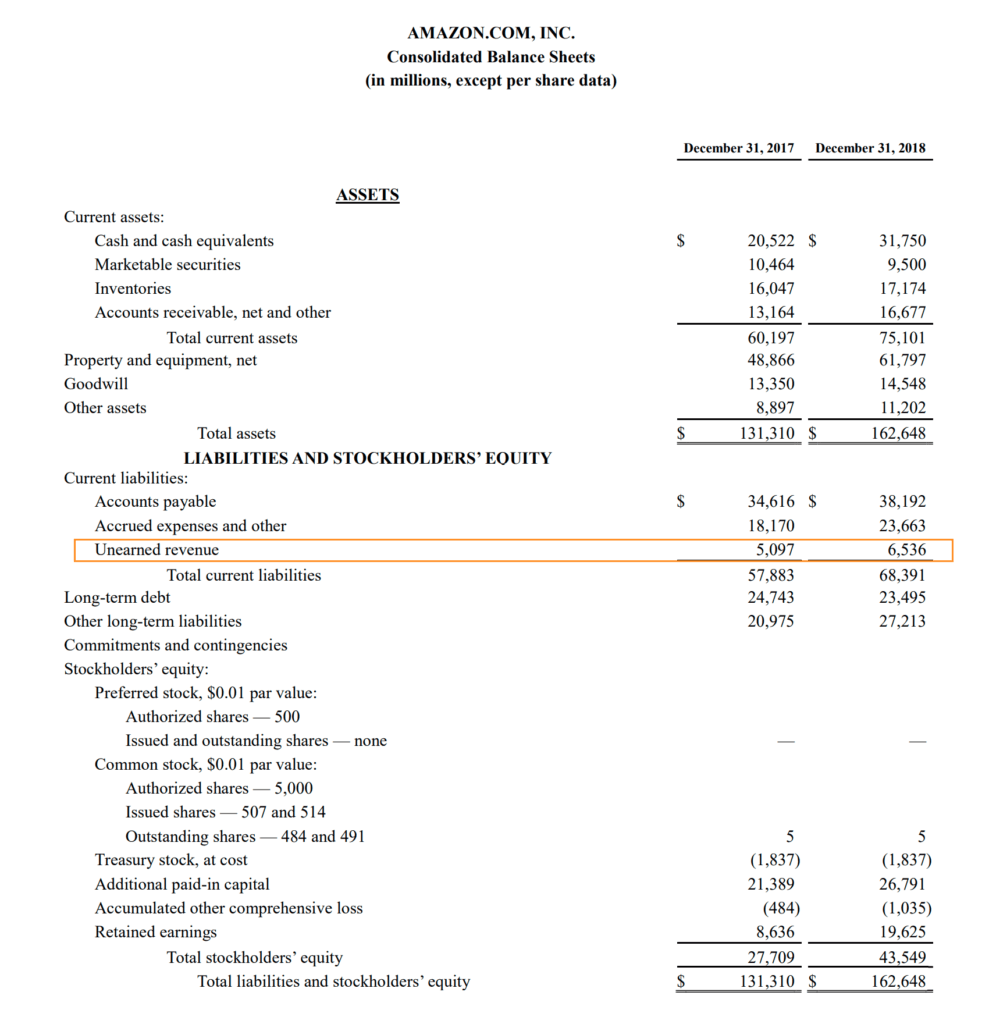
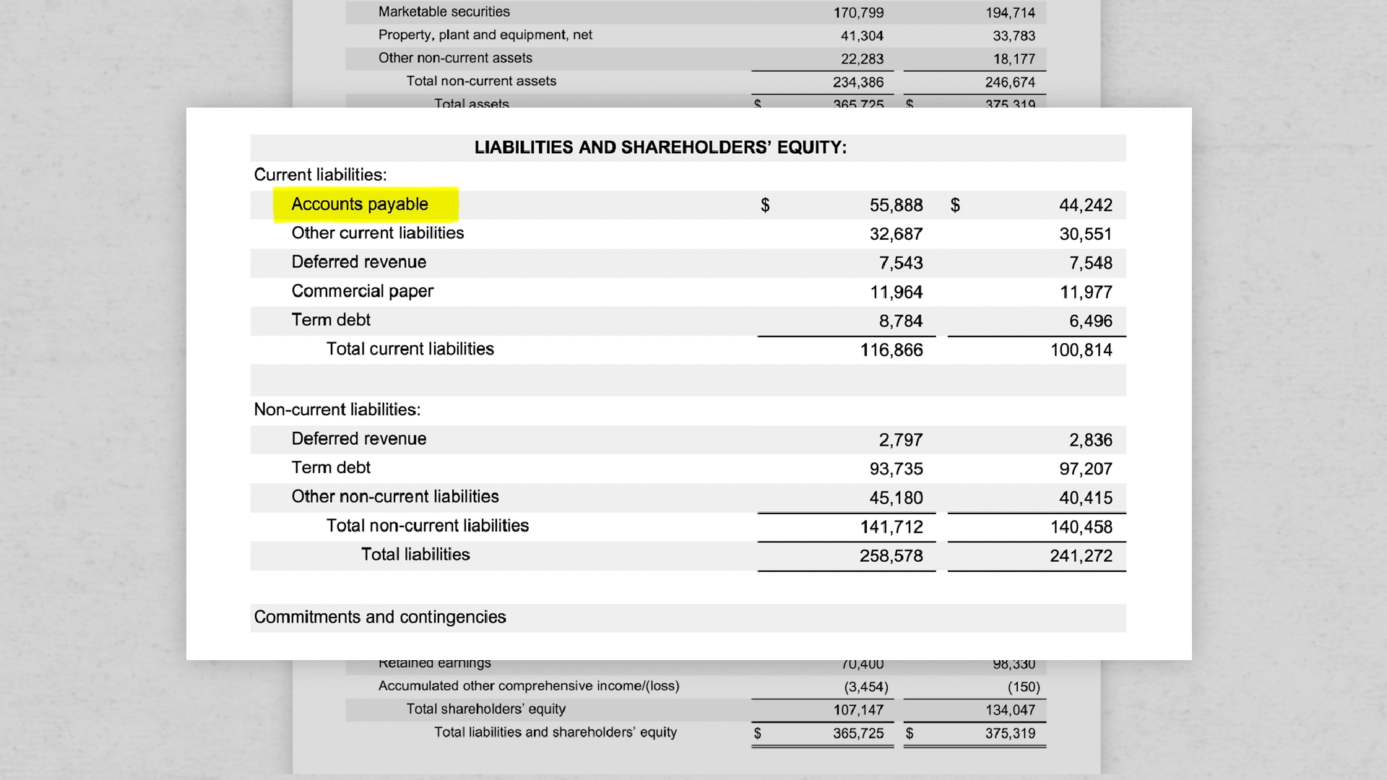
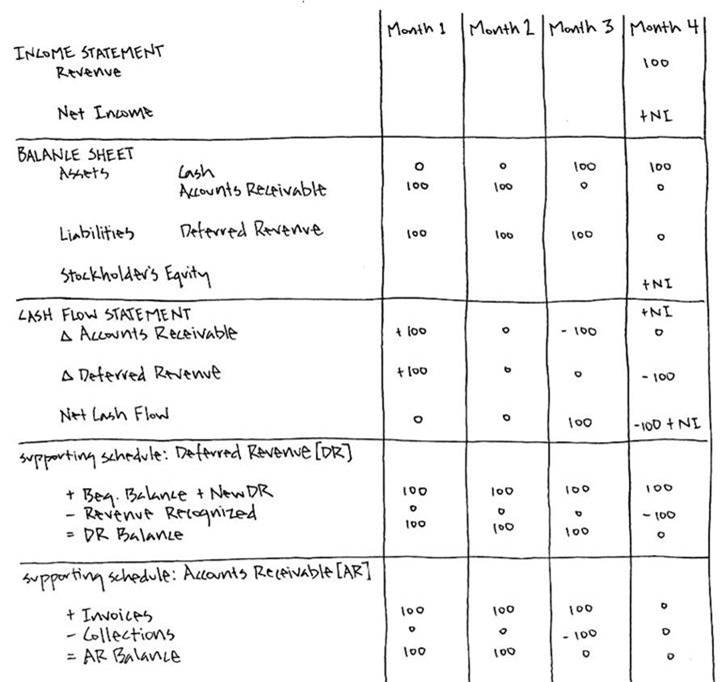
Fundamentally, deferred tax balances represent the future tax impacts of recovering or otherwise consuming assets (e.g., by depreciating the asset) and settling liabilities (e.g.,. On the balance sheet, cash would increase by $1,200, and a liability called deferred revenue of $1,200 would be created. If the effective tax rate is.
It is the opposite of a deferred tax liability,. And, it will be one of the reconciling items you need to input on your tax return (see the. In the balance sheet, paragraph 29.23 of frs 102 requires that deferred tax liabilities are presented ‘within provisions for liabilities’ and deferred tax assets are.
If your capital gains rate is 20. A close look at the term gives you a good idea about the definition. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured at the tax rates that are expected to apply to the period when the asset is.
On august 31, the company would record revenue. All of the information needed to produce a. The $100 is referred to as a temporary tax difference.
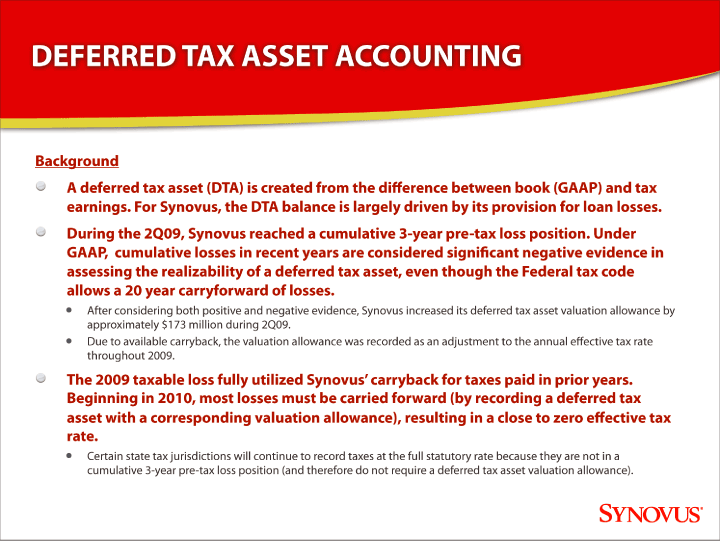
A deferred tax asset is an item on the balance sheet that results from an overpayment or advance payment of taxes. Us financial statement presentation guide 4.5. If you have a cost basis in the asset of $500,000 and you can sell it for $700,000, the appreciation (capital gain) is $200,000.
Here we discuss the top 7. Deferred tax is the application of the.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredcharge.asp_final-6ec4232a769541d8a12246de21ed5927.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferred-credit_final-309c8fbbe2584a3a97d44a9e81c5b62c.png)
